The current furor over President Obama’s broken “keep your plan” promise confusingly melds together two very different claims. The first is a simple question of accuracy and honesty: Obama made a promise about his legislation, the promise has not come true, and a certain level of abuse is deserved. (Karl Rove huffs, “This is a serious breach of trust with the American people.” And you know that Karl Rove takes breaches of presidential trust with the utmost seriousness.)
The justifiable scrutiny of Obama’s veracity has melded seamlessly into a second and very different claim: That Obama’s broken promise is not merely a violation of trust, a fair enough charge, but an act of unfairness to those who have lost their plans.
The health-care debate has suddenly come to focus almost obsessively on the alleged victims of Obamacare, who have lost their cheap individual insurance. Here’s Matthew Fleischer mourning the loss of his bare-bones plan in the Los Angeles Times; here’s David Frum doing the same for the Daily Beast. Mary Landrieu, a vulnerable red-state Democrat, is introducing legislation to ensure that nobody can lose their individual health-care plan.
The idea underlying this notion, while facially appealing, is in fact misguided and morally perverse. No decent health-care reform can keep in place every currently existing private plan.
The New York Times has a helpful graphic displaying the structure of the insurance market:
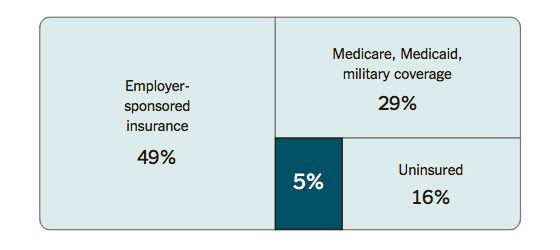
The left and top-right squares show the four fifths of Americans who get coverage through the government. Those on the left who get covered through their employer get tax-subsidized insurance, and those in the top right get insured by the government directly. Obamacare leaves that structure in place (though it has a series of mechanisms designed to hold down their cost inflation).
The main coverage provisions affect the people in the bottom right quadrant. Most of that quadrant lacks any insurance at all, which points to the dysfunctionality of buying individual insurance before Obamacare. Some of them — 5 percent of the population — have a health-insurance plan. Health-care reforms have always thought of the people within that segment as being essentially the same group of people. Those are mainly healthy, non-poor people who have been skimmed out of the insurance pool, leaving behind those too poor, or too likely to need medical care.
Obamacare is designed to pool the bottom-right quadrant into risk pools, somewhat like the people on the left and the upper right. The poorest of the uninsured are eligible for Medicaid, though a Republican Supreme Court and Republican state governments collectively decided to leave them uninsured. The rest have coverage through the new health exchanges. By design, those exchanges prevent insurers from skimming out the healthy and excluding the sick. Some of the 5 percenters will get less expensive health care, mainly because they qualify for tax credits. Others think they will have to pay higher costs but, upon inspection, will be getting cheaper coverage on the exchanges.
But some other portion — an as-yet-undefined fraction of the 5 percent — will actually be paying higher insurance premiums in the exchanges, and their complaints are echoing across the land. Should we feel concerned for their plight? No, we should not, for three reasons.
First, a great many of the people who are happy with their individual health-insurance plan are happy only because they are unaware of its actual value. This sounds patronizing, but it also happens to be demonstrably true. Even highly educated consumers within this market were frequently snookered by insurance plans that turned out to leave them exposed to surprise costs — they incur a sudden high medical cost and discover their plan does not actually cover them. The fine print is a game of wits between insurer and customer that the insurer always wins. A large share of the people telling us now they’re happy with their individual insurance simply haven’t been exposed to a negative surprise. The handful of reporters who closely followed the individual-insurance market before last week are all watching the eulogies for the lost individual plans and having their brains explode.
Second, it is true that some people actually are getting decent individual health insurance, and have to pay more under Obamacare. Before, insurers could charge them a rate based on their individual likelihood of needing medical care, and some people are lucky enough to present a very low actuarial health risk. Now those people will have to pay a rate averaging in the cost of others who are less medically fortunate.
Have those healthy 5 percenters who do have decent insurance “lost” under Obamacare? In the very immediate sense, yes. That is what Obamacare advocate Jon Gruber is getting at when he concedes that 3 percent of Americans will be worse off under the new law. They’ll be paying higher rates in 2014 than they would have.
Yet this takes an oddly narrow view of their self-interest. You may pose a low actuarial risk today, but you cannot be certain your luck will continue for the rest of your life (or until you qualify for Medicare). Even people living the healthiest lifestyles suffer illnesses and accidents, or marry people who have a uterus. Those who are paying a higher rate are getting something for their money: a guarantee that some future misfortune won’t lock them out of the market. You might call such a guarantee “insurance.”
So some of the 5 percenters are wrong, some of them are short-sighted, but they have identified a basic moral principle: Why is it fair to steal from them, the healthy, and give to others, who are sick? If they have truly mastered the fine print of the individual insurance market and want to gamble on remaining a good actuarial risk forever, should they be permitted to keep their winnings? Having drilled down through the practical arguments, here we get to the final reason, the moral bedrock of the issue.
Their objection has an intuitive, libertarian appeal that obscures the fact that the vast majority of insured Americans already submit to this form of redistribution. Indeed, they’re submitting to a much more stringent form of this redistribution. The exchanges are allowed to charge older people up to three times the premium they charge the young. But in the employer system, they’re not allowed to charge older people any higher rate at all. The shift from healthy to sick in the employer insurance pool is massive. Adrianna McIntyre, a 24-year-old wonk prodigy, notes that her employer-based coverage charges her more than three times the rate she could get in the new exchanges.
People accept this transfer from the healthy to the sick because it is the only way to make medical care affordable to the sick. This is a simple mathematical truism. If your medical care costs more than you can afford to pay, the difference must be borne by those whose medical care costs less than they can afford to pay. There are any number of ways to handle this transfer. One is taxes, and Obamacare does use taxes to make insurance more affordable for many of its recipients. There are other potential methods — conservatives like to tout high-risk pools, at least in the abstract — but none escape the basic math.
The healthy 5 percenters do recognize that Obamacare carries out this transfer. Fleischer complains he is “being taken advantage of.” Frum, writing in the same spirit, complains that he must pay $200 more now that insurers can no longer reward him for his excellent health:
That $200 a month differential seems to be the cost of community rating: I had to answer a bunch of questions about my health before qualifying for my prior plan; the new plan will be issued, no questions asked. Presumably somewhere there is a D.C. resident who smokes or who has some pre-existing condition who will receive a corresponding $200 a month windfall.
The complainers are right. But they won’t quite face up to the full implications of their complaint. If you believe the healthy are entitled to keep the financial benefits of their good health, then you must also believe the sick must be denied medical care. Should that principle be the foundation of our health-care system?