The recent spate of protests against police brutality have changed the way the left thinks about rioting. The old liberal idea, which distinguished between peaceful protests (good) and rioting (bad), has given way to a more radical analysis. “Riots work,” insists George Ciccariello-Maher in Salon. “But despite the obviousness of the point, an entire chorus of media, police, and self-appointed community leaders continue to try to convince us otherwise, hammering into our heads a narrative of a nonviolence that has never worked on its own, based on a mythical understanding of the Civil Rights Movement.” Vox’s German Lopez, while acknowledging the downside of random violence, argues, “Riots can lead to real, substantial change.” In Rolling Stone, Jesse Myerson asserts, “the historical pedigree of property destruction as a tactic of resistance is long and frequently effective.” Darlena Cunha, writing in Time, asks, “Is rioting so wrong?” and proceeds to answer her own question in the negative.
The direct costs of violent protests are fairly self-evident. People who may not have anything to do with the underlying grievances get injured or killed, their livelihoods are impaired, the communities in which the rioting takes place suffer property damage that can linger for decades, and the inevitable police response creates new dangers for innocent bystanders. The pro-rioting (or anti-anti-rioting) argument portrays this as the necessary price of worthwhile social change. Rioting can generate attention among people who might otherwise ignore the underlying conditions that give rise to it.
It is surely the case that some positive social reforms have emerged in response to rioting. Lopez highlights the Kerner Commission and diversity efforts in the Los Angeles Police Department. But the question is not whether rioting ever yields a productive response, but whether it does so in general. Omar Wasow, an assistant professor at the department of politics at Princeton, has published a timely new paper studying this very question. And his answer is clear: Riots on the whole provoke a hostile right-wing response. They generate attention, all right, but the wrong kind.
The 1960s saw two overlapping waves of protest: nonviolent civil-rights demonstrations, and urban rioting. The 1960s also saw the Republican Party crack open the New Deal coalition by, among other things, appealing to public concerns about law and order. In 1964, Lyndon Johnson swept every region of the country except the South running a liberal, pro-civil-rights campaign; in 1968, Richard Nixon won a narrower victory on the basis of social backlash.
Determining just what caused the change in public opinion is obviously tricky. Wasow approaches the problem in different ways. One method he uses is to compare the public’s concern for civil rights and its concern for “social control,” with violent and nonviolent protests. They match up pretty closely:
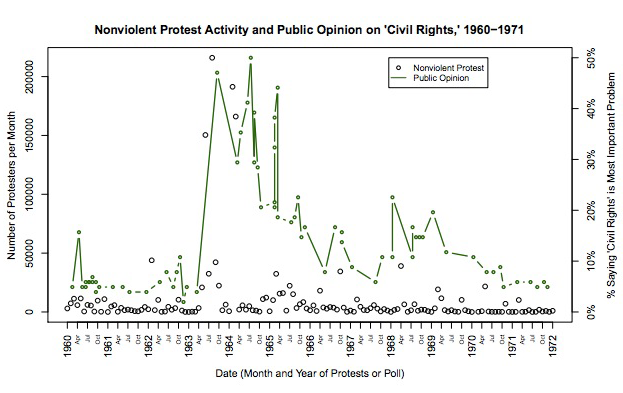
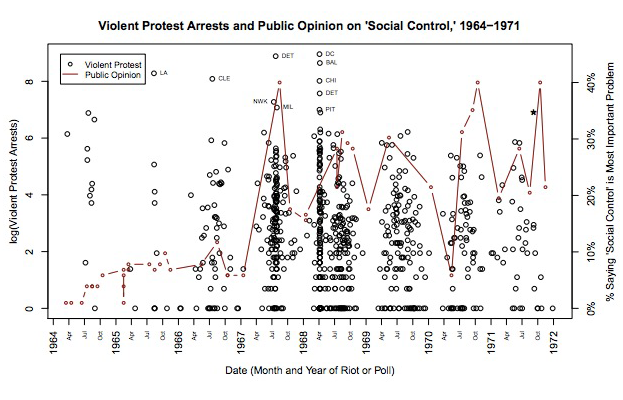
Wasow has another even more persuasive method. He looks at county-by-county voting and compares it with violent and nonviolent protest activity:
Examining county-level voting patterns, I find that black-led protests in which some violence occurs are associated with a statistically significant decline in Democratic vote-share in the 1964, 1968 and 1972 presidential elections. Black-led nonviolent protests, by contrast, exhibit a statistically significant positive relationship with county-level Democratic vote-share in the same period. Further, I find that in the 1968 presidential election exposure to violent protests caused a decline in Democratic vote-share. Examining counterfactual scenarios in the 1968 election, I estimate that fewer violent protests are associated with a substantially increased likelihood that the Democratic presidential nominee, Hubert Humphrey, would have beaten the Republican nominee, Richard Nixon. As African Americans were strongly identified with the Democratic party in this time period, my results suggest that, in at least some contexts, political violence by a subordinate group may contribute to a backlash among segments of the dominant group and encourage outcomes directly at odds with the preferences of the protestors.
Wasow finds that nonviolent civil-rights protests did not trigger a national backlash, but that violent protests and looting did. The physical damage inflicted upon poor urban neighborhoods by rioting does not have the compensating virtue of easing the way for more progressive policies; instead, it compounds the damage by promoting a regressive backlash.
The Nixonian law and order backlash drove a wave of repressive criminal-justice policies that carried through for decades with such force that even Democrats like Bill Clinton felt the need to endorse them in order to win elections. That wave has finally receded and created space for sentencing reforms, demilitarization, an emphasis on community policing, and other initiatives that even have bipartisan support. If the violent protests in Ferguson and Baltimore supercede nonviolent protest, Wasow’s research implies that the liberal moment might give way to another reactionary era.






























